Non-Fungible vs. Fungible tokens
Let’s get specific about some terms. Fungible means something is mutually interchangeable with something exactly like it: if you give someone a dollar bill, they can give you a different dollar bill in return and the value of what you started with doesn’t change. Fungibility is defined by replaceability, meaning that you can replace one fungible item with another and no property of that item is lost.

Non-fungibility is a new feature of the digital landscape. Blockchain technology - with smart contracts and a distributed network of validators - has unlocked the ability for almost anything online to become provably, digitally unique in a safe and reliable way. This was impossible before the invention of Ethereum in 2015, which was the real driver of programmable code that NFTs rely on for their useful properties.
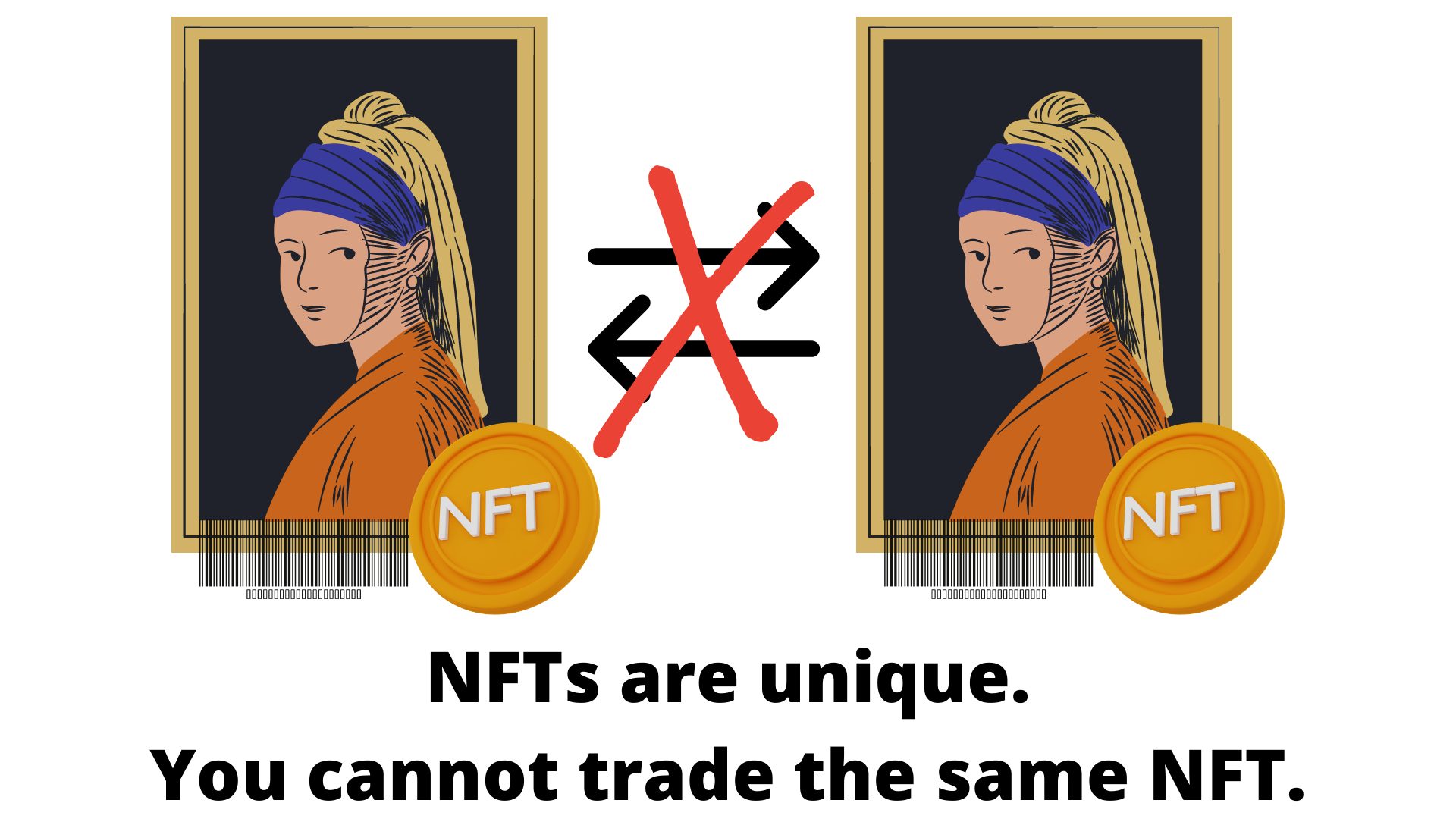
As a result, fungible cryptocurrency tokens like NEAR are being exchanged for non-fungible items. In other words, people are buying digital art with cryptocurrency!
In the next section, we’ll talk about why someone would want to own an NFT and give some examples.
